Commissioning
Commissioning#
Danger
Uncontrolled system movements
During commissioning, and if the radar sensor is part of a control system whose parameters have not yet been set, the system may perform uncontrolled movements. This can endanger people and cause property damage.
- People must stay away from hazardous areas of the system.
- Commissioning only by trained personnel.
- Observe the safety instructions of the system or machine manufacturer.
- Check connectors for secure fit and correct polarity. Replace damaged connectors.
- Switch on the system.
Electrical connection#
The supply voltage is 15…30 VDC.
For further details, see the IO-Link configuration manual.
Notes on operation#
Caution
High-frequency electromagnetic waves
The antenna of the radar sensor emits high-frequency electromagnetic waves.
To avoid health hazards, additional measures must be taken.
- Position the antenna so that a safety distance of at least 20 cm between the antenna and workplaces is ensured.
- Ensure that people do not stay in the immediate vicinity of the antenna for extended periods.
Info
If pin 2 is used as a switching output, the maximum current limitation must be observed (see Technical Data).
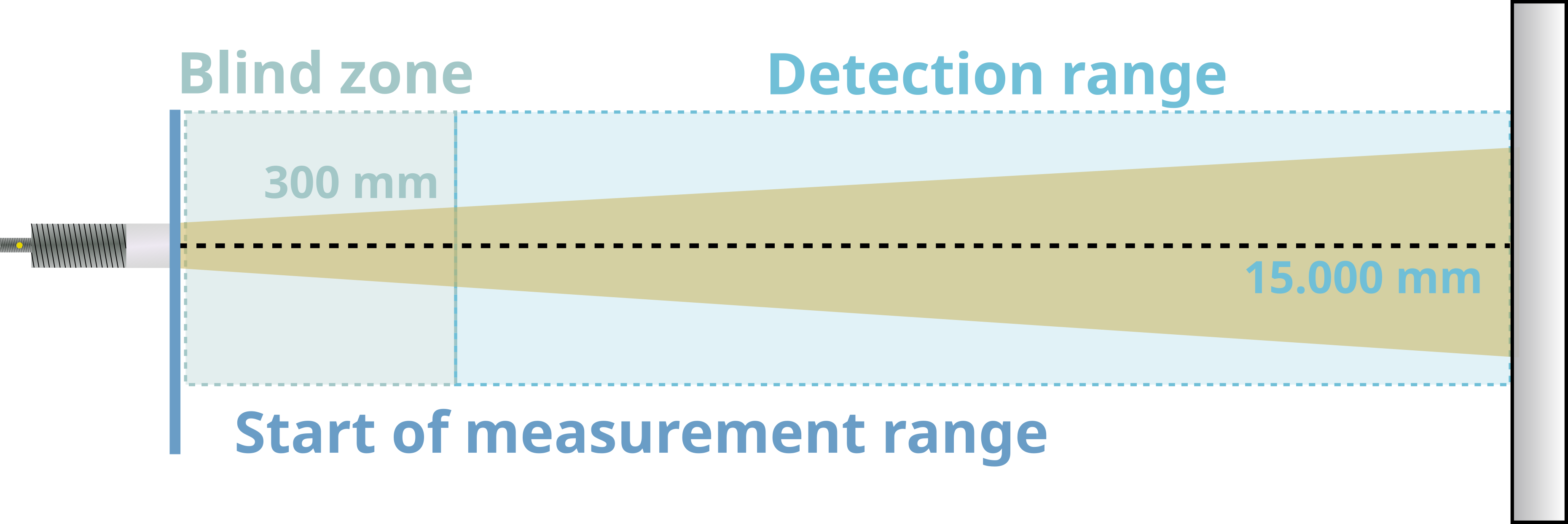
Sensor detection ranges#
Blind zone:
- No object detection takes place in the blind zone. This area should be kept clear for reliable measurements.
- Objects in the blind zone can cause false reflections and incorrect distance values.
- Thin materials with low absorption, such as plastic or glass, can be placed and penetrated in the blind zone, e.g., to protect the sensor against mechanical influences. This must be tested individually.
- In radar reflex-gate mode, depending on the object properties, it is possible to detect objects within the blind zone.
Detection range:
- Objects are detected if their radar cross-section is sufficient for radar reflections and the alignment is suitable.
- The maximum range is achieved under the conditions specified in the data sheet.
- Measurements outside the detection range have not been tested. Use outside the detection range is at your own risk.
The following standardized target objects are used for radar sensor calibration:
| Target object | Width/Diameter [m] | Depth [m] | Radar cross-section [m²] | Reflection strength [dB] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large radar corner reflector (metal) | 0.212 | 0.150 | 84.82 | 19.29 |
| Medium radar corner reflector (metal) | 0.071 | 0.050 | 1.05 | 0.20 |
| Small radar corner reflector (metal) | 0.047 | 0.033 | 0.20 | -7.02 |
| Metal sphere | 0.120 | - | 0.01 | -19.47 |
Reflectivity and typical radar cross-sections#
Microwaves behave similarly to light due to their small wavelength and show effects such as diffraction, total reflection, mirroring, and interference. These effects are crucial for understanding the properties of radar sensors. An emitted wave is diffusely scattered at an object, with part of the wave being reflected back to the sensor. The strength of this reflection depends on the nature and material of the object.
The radar cross-section indicates how much of the radar signal is reflected by an object back towards the source. It depends on the size, shape, and material of the object. Larger objects with a smooth surface are easier to detect because they have a higher radar cross-section.
A human target has a lower radar cross-section compared to a metal object and is therefore a less effective radar target.
Material dependence
Radar waves propagate unhindered in a vacuum. When they hit an object, the signal changes depending on the nature of the object. Depending on the material, radar waves are completely or partially absorbed or reflected. They can also penetrate various substances.
In summary, absorbing materials are less suitable as radar targets. Although they create a reflection due to the "material jump," most of the radar wave energy is absorbed.
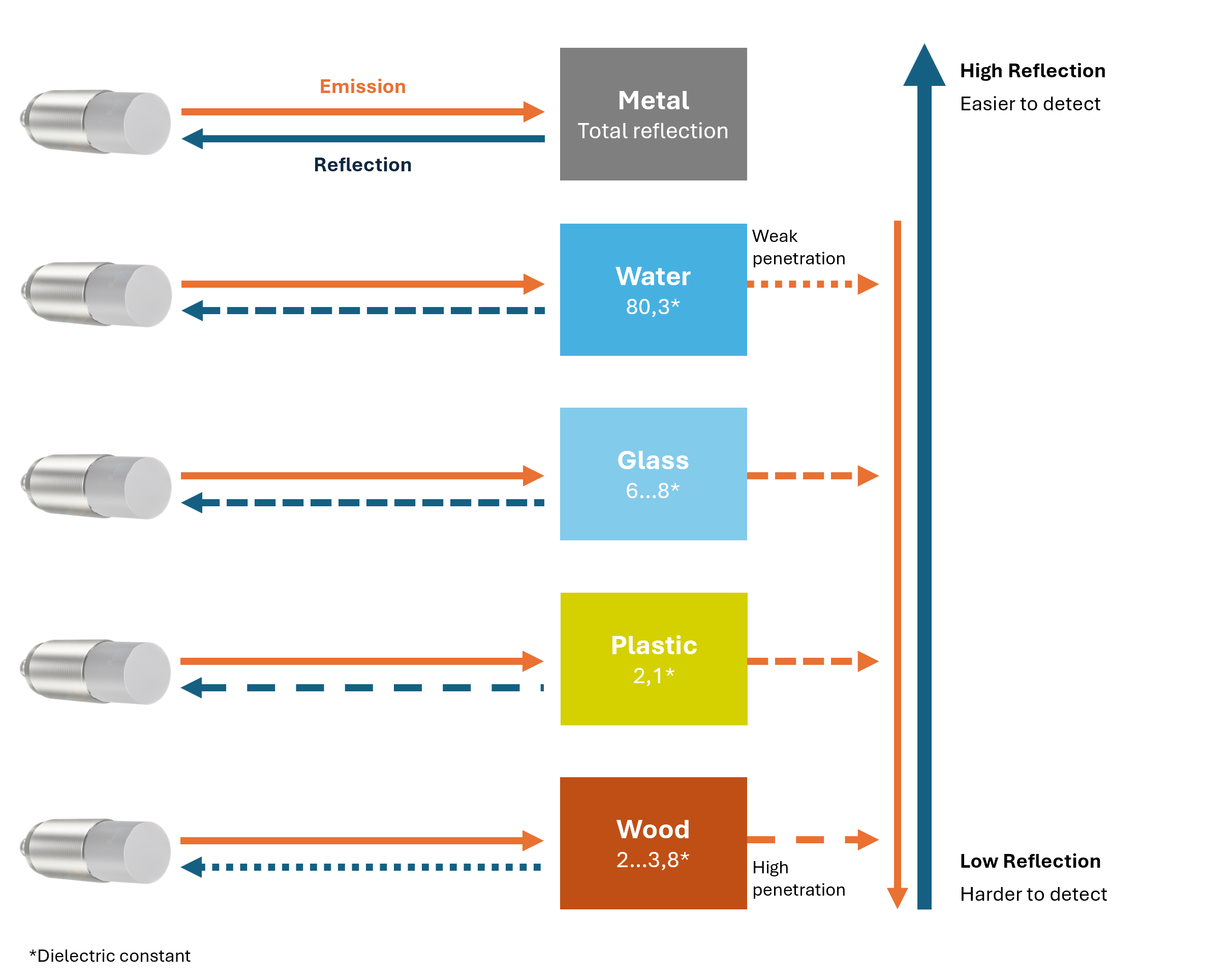
The dielectric constant plays an important role in radar sensors, as it influences the propagation of electromagnetic waves in the material. The dielectric constant is the ratio of the electric field strength in a vacuum to the field strength in the material.
Here are some relevant points:
Material selection
Materials with a high dielectric constant can improve the efficiency of radar sensors by optimizing waveguiding and signal strength.
Signal processing
The dielectric constant influences the reflection and absorption of radar waves, which is crucial for the accuracy and range of the sensors.
Dielectrics (non-conductive materials)
- With \(\varepsilon_r > 1\), e.g., plastics, glass, paper, ceramics
- Reflectivity depends on \(\varepsilon_r\)
- Partial transmission, partial absorption
- With \(\varepsilon_r >> 1\), e.g., plastics, glass, paper, ceramics
- Materials with high absorption (e.g., water) can completely absorb radar waves
- With \(\varepsilon_r \approx 1\), e.g., air, vacuum
- No attenuation, completely transparent to radar waves
Table with the properties of various materials regarding absorption, reflection, and penetration of radar waves:
| Material | Absorption | Reflection | Penetration of Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | None | Total reflection with direct incidence; refraction and partial reflection possible with oblique incidence | None |
| Wood | Medium to strong (depending on moisture content) | Low | Low |
| Water | Very strong | Partial or total reflection possible (depending on angle of incidence) | None, due to absorption |
| Foams | Low | Low | Very low |
| Plastics | Low to high (depending on thickness and type of plastic) | Low to high (depending on thickness and type of plastic) | Low to high (depending on thickness and type of plastic) |
| Glass | Low to high (depending on thickness of glass) | Low to high (depending on thickness of glass) | Low to high (depending on thickness of glass) |
| Clothing | Medium to strong (depending on moisture content) | Low | Low |
| Rain | Low | Low | Very good |
| Humans | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Ice | Very high | Partial or total reflection possible (depending on angle of incidence) | None, due to absorption |
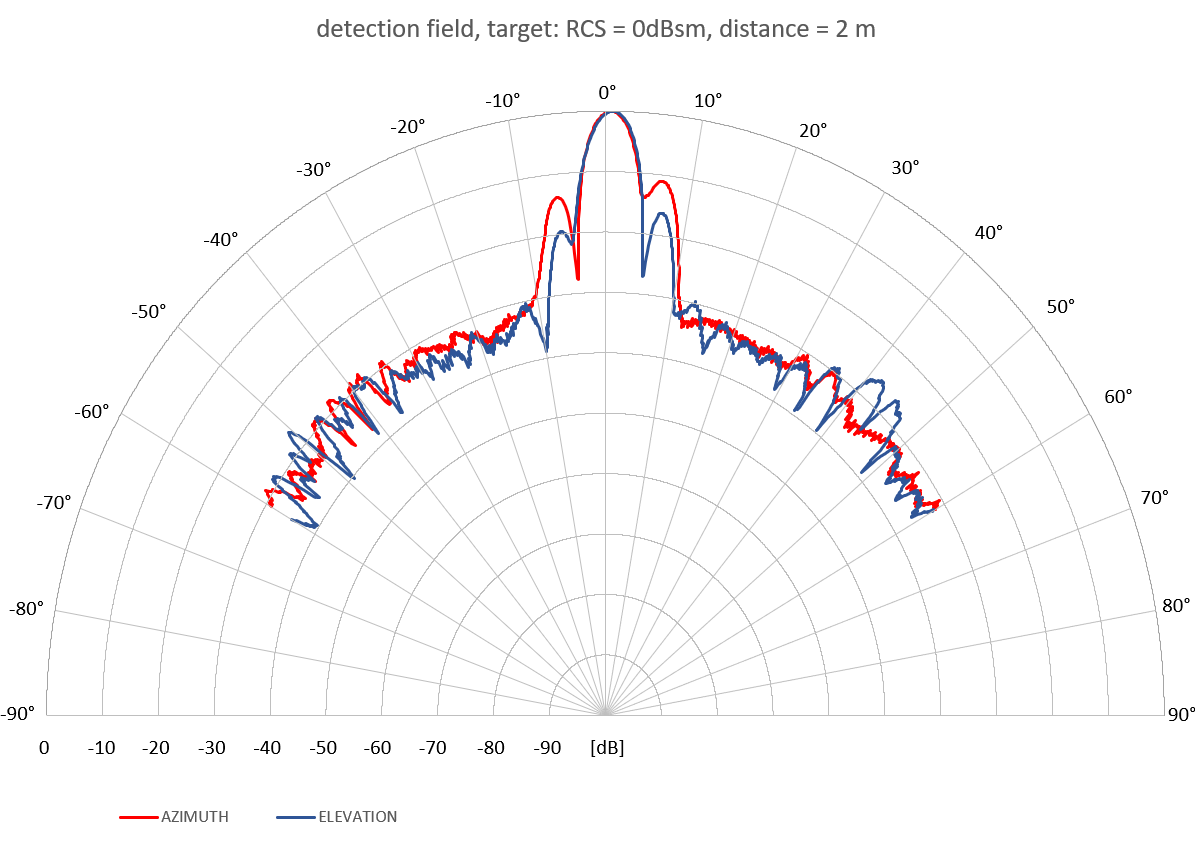
Detection range of the radar sensor#
Cleaning#
The radar sensor can be cleaned with a high-pressure cleaner. During cleaning, the radar sensor may not reliably detect a target.
The front cap of the radar sensor can be cleaned with a soft cloth if necessary.
Maintenance#
The product is maintenance-free.